It’s World Diabetes Day 2024!
Every year, World Diabetes Day shines a spotlight on a condition that affects millions globally. This year’s theme, “Breaking Barriers, Bridging Gaps,” encapsulates the urgent need to address the disparities in diabetes care and management. As the world commemorates the 100th anniversary of the discovery of insulin, we reflect on the progress made and the challenges that lie ahead in combating this chronic disease. The World Health Organization’s launch of the Global Diabetes Compact marks a significant milestone in this journey, aiming to create equitable access to diabetes care worldwide.
World Diabetes Day 2024 – The Global Burden of Diabetes
Diabetes is not just a health issue; it’s a global epidemic. The numbers are staggering, with an estimated 537 million adults living with diabetes worldwide. This figure is projected to rise to 643 million by 2030. The condition is characterised by chronic high blood glucose levels, leading to serious health complications if not managed properly. There are three main types of diabetes, each with its unique challenges and management strategies.
Type 1 Diabetes: Often diagnosed in childhood, type 1 diabetes results from the pancreas’s inability to produce insulin. It is an autoimmune condition that requires lifelong insulin therapy. Patients face daily challenges of balancing insulin doses with dietary intake and physical activity.

Type 2 Diabetes: Accounting for about 90% of all diabetes cases, type 2 diabetes is largely preventable. It is characterised by the body’s ineffective use of insulin, often linked to obesity, poor diet, and lack of physical activity. The rise in type 2 diabetes among younger populations, including children and adolescents, is particularly alarming.
Gestational Diabetes: This form of diabetes occurs during pregnancy and poses risks to both mother and child. Women with gestational diabetes are at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Preventing Diabetes: A Collective Responsibility
The prevention of diabetes, especially type 2, hinges on addressing modifiable risk factors. Public health initiatives focusing on promoting healthy lifestyles are crucial. Here are some key strategies:
Healthy Diets and Physical Activity: Encouraging balanced diets rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and regular physical activity, can significantly reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.

Education and Awareness: Increasing awareness about the importance of maintaining a healthy weight and active lifestyle is essential. Schools, workplaces, and communities play a vital role in promoting these messages.
Early Intervention: For individuals with prediabetes or those at high risk, early interventions can prevent the progression of type 2 diabetes. This includes lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medication.
Managing Diabetes: Bridging the Gaps
Effective management of diabetes is critical to preventing complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, blindness, and amputations. Yet, disparities in access to care remain a significant barrier. The WHO Global Diabetes Compact aims to address these gaps by ensuring that everyone with diabetes receives the care they need.
Equitable Access to Treatment: One of the core goals of the Compact is to provide affordable and comprehensive care to all people with diabetes. This includes access to insulin, oral medications, and necessary medical devices.
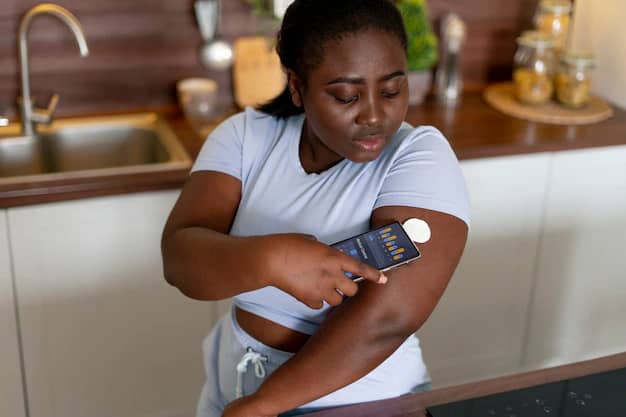

Integrated Care: Effectively managing diabetes requires a holistic approach. This includes regular monitoring of blood glucose levels, managing comorbid conditions like hypertension and hyperlipidaemia, and routine screenings for complications such as retinopathy and neuropathy.
Support Systems: Empowering patients through education and support systems is vital. Therapeutic patient education helps individuals manage their condition better, improving outcomes and reducing healthcare costs.
The Road Ahead: Breaking Barriers
As we celebrate the strides made in diabetes care, it is crucial to acknowledge the work that still needs to be done. The vision of the WHO Global Diabetes Compact is clear: reduce the risk of diabetes, ensure equitable access to care, and prevent complications through comprehensive public health strategies.
Innovative Solutions: Technology advancements, such as continuous glucose monitors and insulin pumps, are transforming diabetes management. Making these innovations accessible to all patients, regardless of their socioeconomic status, is a priority.
Policy and Advocacy: Governments and health organisations must collaborate to implement policies that support diabetes prevention and care. This includes integrating diabetes management into universal health coverage packages.
Community Engagement: Local communities play a crucial role in supporting individuals with diabetes. From peer support groups to community health programmes, grassroots efforts are essential in creating a supportive environment for those affected by diabetes.
World Diabetes Day 2024 – Current Diabetes Statistics
The State of Diabetes Today
As we mark World Diabetes Day, it is essential to reflect on the current state of diabetes globally.
Europe has the highest burden of type 1 diabetes globally with an estimated 1 in 3 people living with diabetes remaining undiagnosed and up to half may not meet their treatment targets.
Some types of diabetes can be prevented by targeting risk factors with interventions such as improving nutrition, increasing physical activity, reducing obesity, reducing tobacco use and providing more health-supporting environments.
Many diabetes risk factors are related to socioeconomic status and the impact of social, economic and environmental determinants of health.
World Diabetes Day is not just a date on the calendar; it is a call to action. By breaking barriers and bridging gaps, we can create a world where everyone affected by diabetes has access to the care and support they need. Join the global movement to raise awareness, spread knowledge, and make lasting changes in the fight against diabetes.
